Our Technology
The Opportunity
The importance of accurate and timely needle-tip positioning at the point of care cannot be overstated in the >200 million needle-based procedures performed globally each year.
Misinterpretation and misplacement of the needle-tip during percutaneous biopsy, regional anaesthesia, or even intratumoural drug delivery procedures can result in repeat procedures, delayed or sub-optimal therapy, and even severe complications.
Failed biopsies through insufficient tissue samples or false-negative pathology results in breast (>2%2), liver (7%3), and lung (4%4) generate critical delays to treatment and increase associated healthcare costs to both the provider and patient, whilst failed regional anaesthesia procedures may result in significant complications such as nerve damage 1, local anaesthetic toxicity1, and pneumothorax1.
The mean acceptable needle placement error in targeted lesions is considered as small as 2.7 mm by interventional radiologists, whereas the mean maximal encountered unwanted needle bending in interventional procedures is 5.3 mm5. This implies that unwanted needle bending, which is only one complicating factor in needle placement, is higher than that considered acceptable. Current needles in interventional radiology need improvement, according to 95% of interventional radiologists (IRs)5.
With biopsy procedures costing between $1500 and $30006 (e.g. liver), additional clinical time for re-do procedures resulting from errors or re-admissions costs healthcare providers even more.
The Solution
Active Needle's goal is to bring the benefits of ultrasonic needles to healthcare and aligned markets. The revolutionary technology aims to improve medicine by improving therapy and reducing burdens on patients and healthcare providers. Whether by reducing errors from misplaced and failed needle procedures, revolutionising intra-tumoural injections in cancer therapy, or simply reducing needle pain, Active Needle strives to make a profound difference in the clinic.
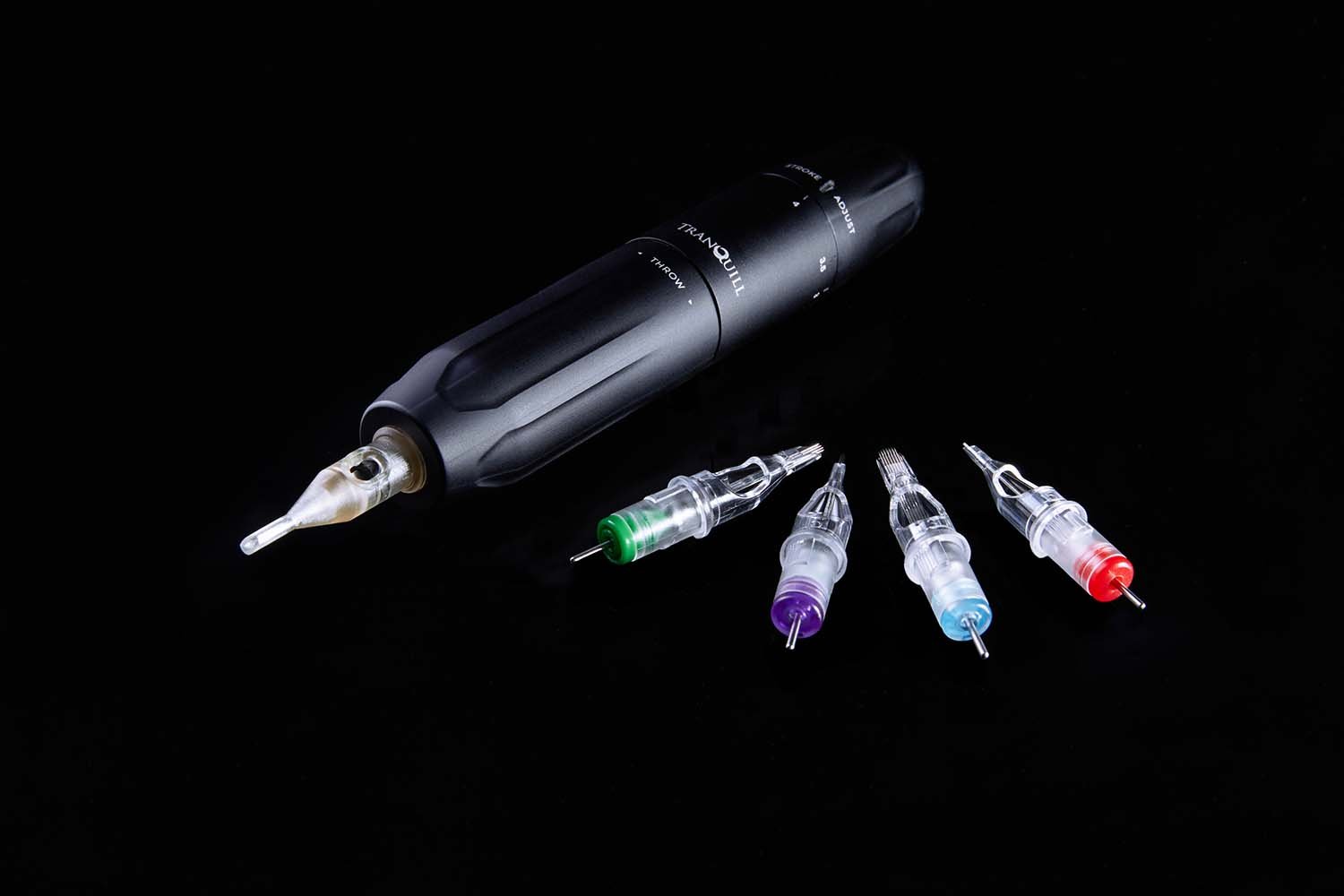
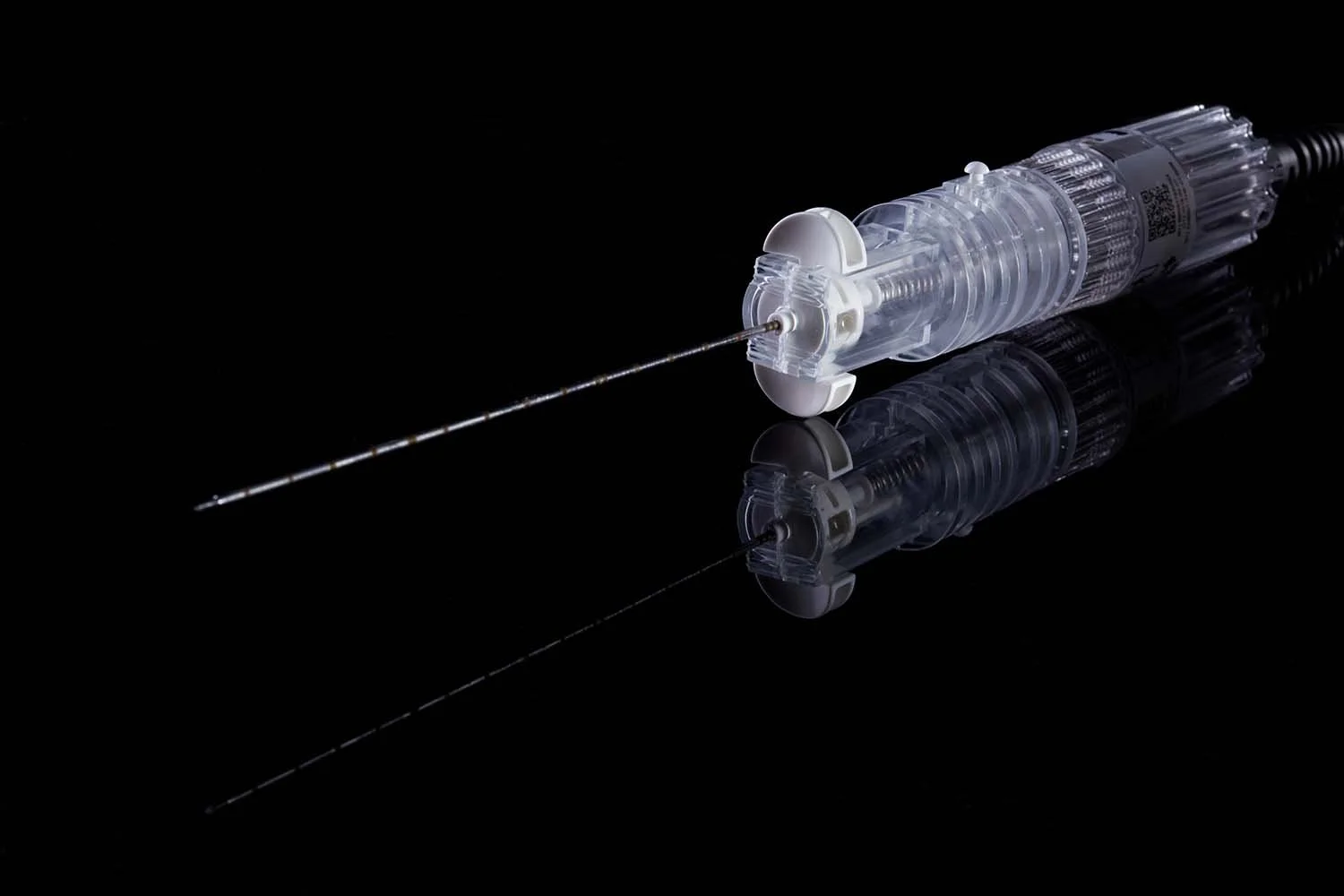
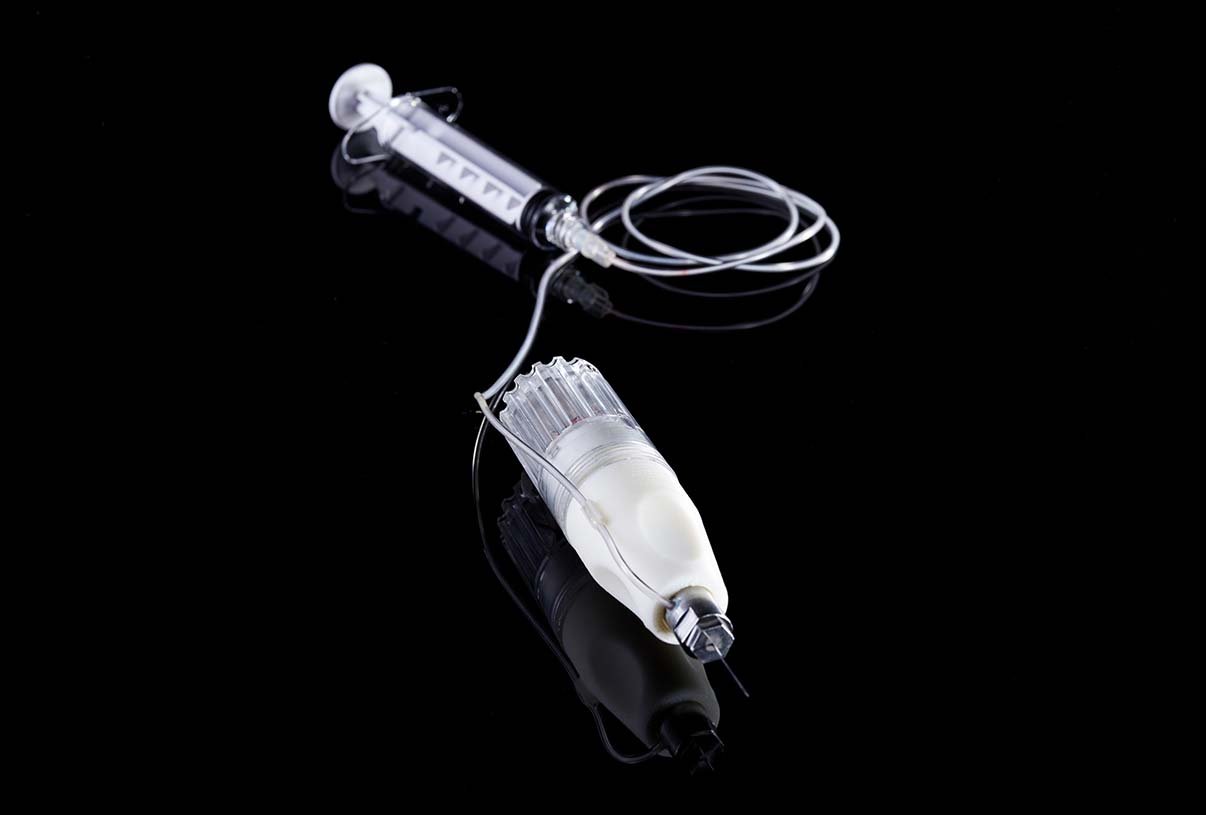
The Technology
Active Needle's innovative ultrasonic technology, co-invented by Dr Muhammad Sadiq, induces high frequency pulsation. This short, but highly rapid movement conveys a number of important properties to our needles facilitating several clinical benefits, such as enhanced visibility, reduced pain and trauma, and improved drug distribution. The technology promises reduced in-hospital costs and time, a better patient experience, and the upskilling of less experienced users, allowing more efficient use of finite medical resources.
A Revolutionary Step
Active Needle’s goal is to reduce the significant physical and monetary cost paid by patients and providers from errors and re-admissions associated with misplaced and failed needle procedures.
Collaborative Development
At Active Needle Technology, the patient, clinician and payer inform both our device design and therapy targeting. Devices are developed with clinicians to improve outcomes and be both easy to use and make economic sense. Devices are typically in two parts: a sterile disposable component and a non-disposable. In this way, we can focus on efficiency, cost reduction and minimising the amount of single-use material used.
Unrivalled Needle Visibility
Active Needle Technology allows important features of the needle to be visible under Doppler ultrasound even at challenging angles and deep tissue locations.
The Doppler technique, routinely used for blood flow measurements, generates a colour-coded map of needle velocity superimposed on the grey-scale images of tissue anatomy.
ANT’s ultrasonic needle technology can be activated or de-activated at the clinician’s discretion, offering complete control during needle placement.
Enhanced Therapeutics
Ultrasonic intratumoural delivery can significantly enhance perfusion and deposition rates of a variety of therapeutic agents.
With its operation similar to a micro-pneumatic drill, Active Needle Technology demonstrated reduced levels of needle penetration forces under laboratory conditions, especially at the first puncture phase. Measurements in ex-vivo animal tissue and cadaver confirmed that ultrasound vibration reduces peak penetration force by >70%7.
The resulting effect may not only reduce tip deflection, but may also facilitate better penetration through tissue interfaces, contributing to reduced pain and tissue trauma. Measurements in gelatine phantom confirmed that ultrasound vibration reduces tip deflection by >30%8.
Reduced Needle Penetration Force and Deflection
1. Xia, W. Mari, JM. West, SJ. Ginsberg, Y. David, AL. Ourselin, S. Desjardins, AE.: In-plane ultrasonic needle tracking using a fiber-optic hydrophone. Med. Phys. 42 (10), October 2015. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26429273 /
2. Boba, M. Kołtun, U. Bobek-Billewicz, B. Chmielik, E. Eksner, B. Olejnik, T.: False-negative results of breast core needle biopsies – retrospective analysis of 988 biopsies. Pol J Radiol. 2011 Jan-Mar; 76(1): 25–29. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3389906
3. Vernuccio, F. Rosenberg, MD. Meyer, M. Choudhury, KR. Nelson, RC. Marin, D.: Negative Biopsy of Focal Hepatic Lesions: Decision Tree Model for Patient Management. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2019 Mar;212(3):677-685. Epub 2019 Jan 23. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30673333/
4. Zhao, Z-L. Peng, L-L. Wei, Y. Li, Y. Wang, GM. Yu, M-A.: The accuracy of ultrasound-guided lung biopsy pathology and microbial cultures for peripheral lung lesions. J Thorac Dis. 2020 Mar;12(3):858-865. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32274153
5. de Jong, TL. van de Berg, NJ. Tas, L. Moelker, A. Dankelman, J. van den Dobbelsteen, JJ.: Needle placement errors: do we need steerable needles in interventional radiology? Med Devices (Auckl). 2018; 11: 259–265. Published online 2018 Aug 3. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6080661
6. Allen, AM. van Houten, HK. Sangaralingham, LR. Talwalkar, JA. McCoy, RG.: Healthcare Cost and Utilization in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Real-World Data From a Large U.S. Claims Database. Hepatology, VOL. 68, NO. 6, 2018. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29774589/
7, 8. Liao, X. ‘Investigation of Needle-Tissue Interaction during Ultrasonic Needle Intervention.’ University of Dundee. July 2015. P.119. p.122.
9. Active Needle Technology Ltd. Data on file. 2023.

Active Needle Benefits
Unrivalled
Visibility
Ultrasonic technology provides unrivalled needle visibility during ultrasound guidance in Doppler mode, helping the operator to avoid critical deep-tissue structures.
Reduced
Pain
Vastly reduced needle penetration forces, especially during the initial skin puncture, can result in less pain and trauma to tissue and an improved patient experience.
Less
Deflection
Ultrasonic vibration facilitates more efficient needle-tip penetration through tissue interfaces, even at challenging angles and deeper anatomical locations. This can lead to more accurate placement.
Enhanced
Therapeutics
Ultrasonic intratumoural delivery can significantly enhance perfusion and deposition rates of a variety of therapeutic agents.